旋转的例子

图形学中向量的默认形式是列向量
叉乘公式
$$
\vec{a} \times \vec{b}=\left(\begin{array}{l}
y_{a} z_{b}-y_{b} z_{a} \\
z_{a} x_{b}-x_{a} z_{b} \\
x_{a} y_{b}-y_{a} x_{b}
\end{array}\right)
$$
$$
\vec{a} \times \vec{b}=A^{*} b=\left(\begin{array}{ccc}
0 & -z_{a} & y_{a} \\
z_{a} & 0 & -x_{a} \\
-y_{a} & x_{a} & 0
\end{array}\right)\left(\begin{array}{l}
x_{b} \\
y_{b} \\
z_{b}
\end{array}\right)
$$
$$
\begin{array}{l}
\vec{x} \times \vec{y}=+\vec{z} \\
\vec{y} \times \vec{x}=-\vec{z} \\
\vec{y} \times \vec{z}=+\vec{x} \\
\vec{z} \times \vec{y}=-\vec{x} \quad \vec{a} \times(\vec{b}+\vec{c})=\vec{a} \times \vec{b}+\vec{a} \times \vec{c} \\
\vec{z} \times \vec{x}=+\vec{y} & \vec{a} \times(k \vec{b})=k(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}) \\
\vec{x} \times \vec{z}=-\vec{y}
\end{array}
$$
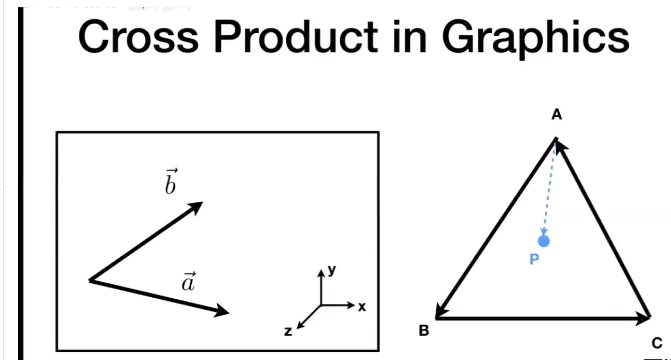
叉乘可以定义左右和形状的内外两侧信息,起到定向的作用
$$
\begin{array}{l}
\vec{a} \times \vec{b}=+\vec{z} \quad \quad a在b的左侧 \\
\vec{b} \times \vec{a}=-\vec{z} \quad \quad a在b的右侧\\
\vec{AB} \times \vec{AP}=+ \\
\vec{BC} \times \vec{BP}=+ \\
\vec{CA} \times \vec{CP}=+ \quad \quad 如P点在AC右侧,则\vec{CA} \times \vec{CP} 为负值 \\
如三角行逆时针,只要所有的叉乘值都为正值或都为负值就可判断在三角形内部,从而忽略给定的三角形的顺序 \\
在边上的情况被称为 corner case 这时候开发者自己说了算\
\\
\end{array}
$$
虚拟机安装问题
Not in a hypervisor partition (HVP=0) (VERR_NEM_NOT_AVAILABLE).
AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS (or by the host OS) (VERR_SVM_DISABLED).
解决方法
1.Windows设置 - 更新和安全 - 回复 - 立即重新启动
2.Troubleshoot -> Advanced option – > UEFI Firmware Settings -> Restart
3.在BIOS中找到Virtualization 选项,它常位于Advanced 或 System Configuration 选项卡下
4.设置Virtualization 的状态为Enabled。
AMD和Intel的设置不一样
Eigen库的使用问题
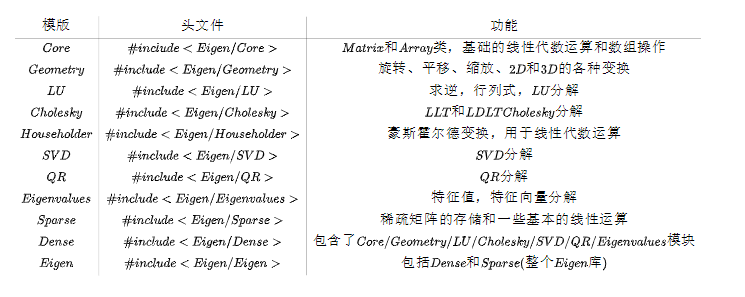
Eigen库的使用用例
1 |
|